The phase behavior of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients in multi-component pharmaceutical systems, during the various stages of freeze-drying, is a complex interplay of formulation variables and processing conditions. Rational drug product and process development necessitate: (i) a thorough characterization of the phase transitions of API and the excipients in the frozen state and during freeze-drying, (ii) gaining an understanding of the crystallization tendency of API and excipients during processing including the effect of annealing, and (iii) identifying the physicochemical stability requirements and critical quality attributes of the product. The use of two commonly used techniques, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffractometry, is complementary and often provides a deep insight into the physical chemistry of freeze-drying. Four case studies will be presented and will deal with: (i) crystallization of the widely used lyoprotectant, trehalose, (ii) controlling the physical form of mannitol crystallizing from solution during cooling, (iii) in situ salt formation during freeze-drying and (iv) salt disproportionation during freeze-drying due to pH shift in frozen solutions. In each case, the potential implications on product performance will be discussed. Presented by Raj Suryanarayanan, PhD Professor at the College of Pharmacy, University of Minnesota
-
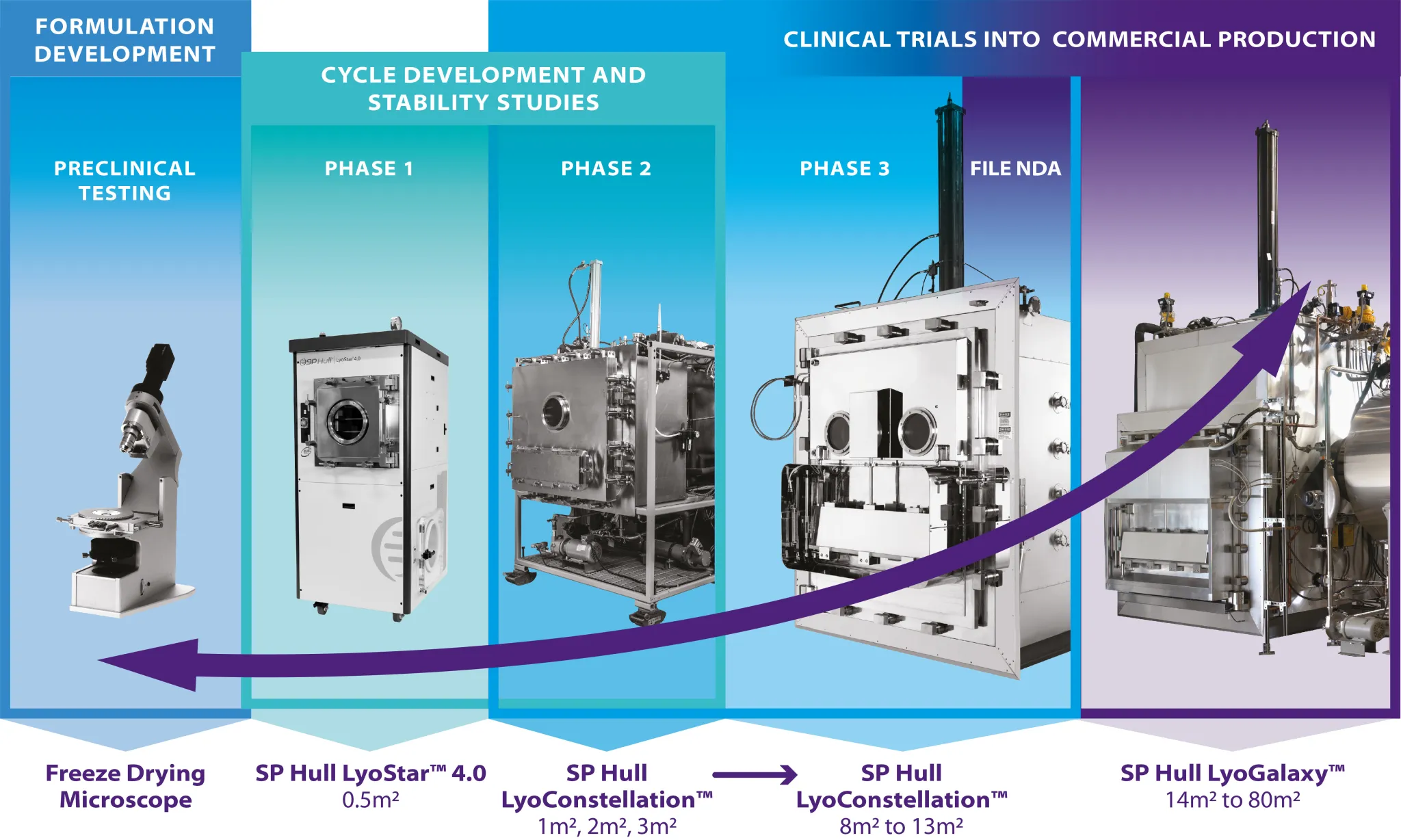
Products Pharmaceutical Processing Equipment Fill-Finish / Aseptic Processing Equipment Aseptic & Production-Scale Freeze Dryers Lyophilization Technology & PAT Tools
-
Applications
Find Products by Applications & Industries
- Brands
-
Learning Lab
Explore the Learning Lab
- Service & Support
-
About Us
Learn more about SP