Lyophilization is an effective approach to improve the storage stability of nanomedicines. The freezing step of the lyophilization process can impact nanoparticle stability due to increased particl

Surfactants are widely used in frozen and freeze-dried protein formulations to prevent ice-surface-induced destabilization. Polysorbates (PS), especially PS20 and 80, are commonly used in protein p

Mannitol is a popular excipient in lyophilized injectable small and large molecule formulations. Mannitol crystallizes readily in aqueous solutions enabling primary drying at elevated temperature,

Product temperature is the most critical parameter during lyophilization; however it is rarely measured during commercial GMP production of sterile injectable pharmaceuticals. With Tempris® wirele

When prelyophilization solutions are frozen, selective crystallization of a buffer component is known to cause a pH shift, which can sometimes be pronounced. Such pH shifts have been reported with

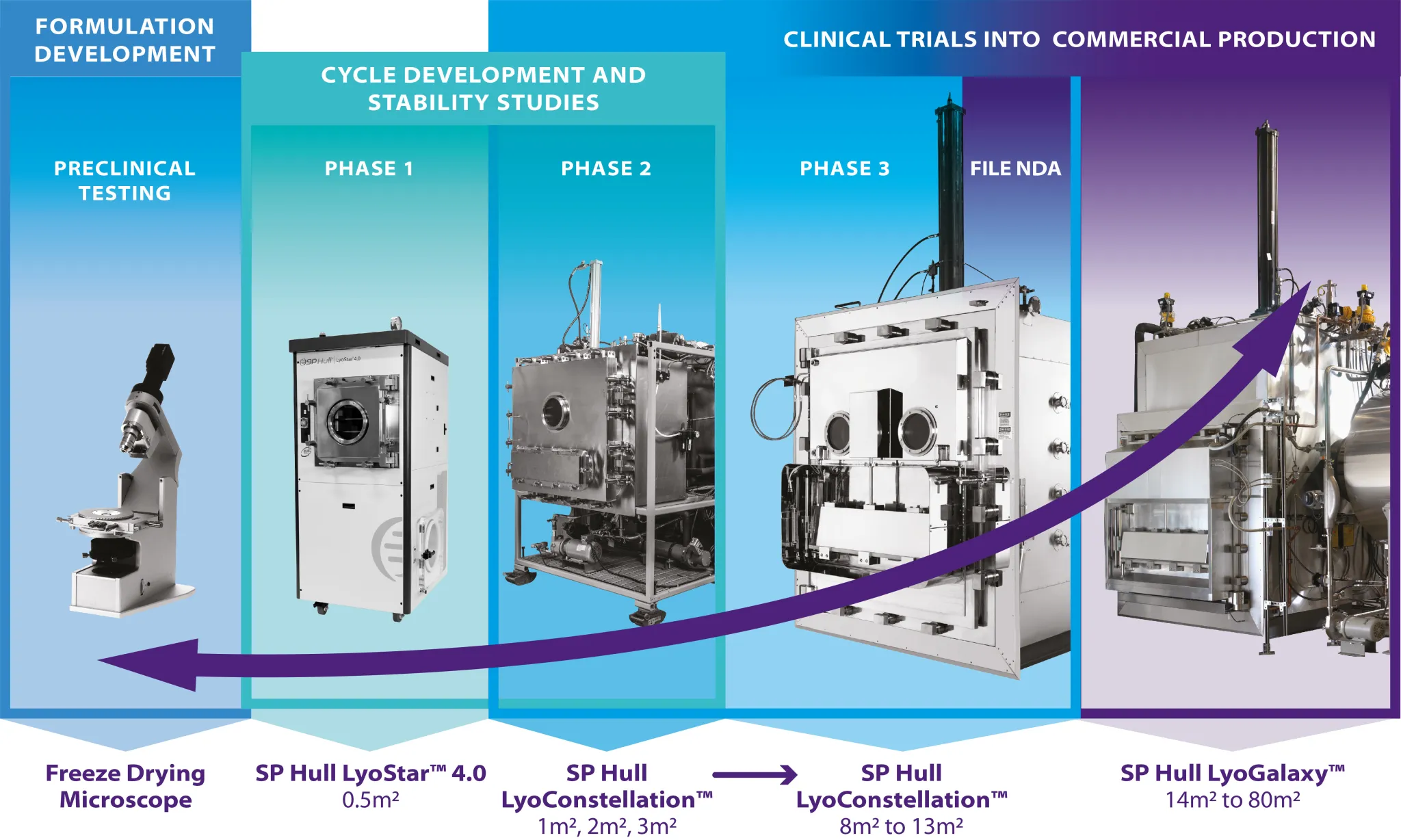
Successfully transferring the manufacturing process across lyophilizers, especially for scale-up, requires a knowledge of the drying kinetics of the product. Experimental approaches to determine th

Small batches of lyophilized products can be prepared aseptically and maintain their sterility while using a non-sterilizable freeze-dryer. This webinar will discuss the techniques for preparing th

Automated inspection of lyophilized products was in its infancy in the 1990’s, but has become widely accepted in the 21st century. With advances in computers, cameras and machine learning, many o

Vial fogging is a phenomenon commonly observed in lyophilized biologic drug products and has been widely reported in the pharmaceutical industry. Vial fogging presents as a haze of dried powder whi

The use of nanoparticles (under 100 nm) in recent years has increased significantly, with applications in contrast agents in medical imaging, carriers for gene delivery into cells, targeted deliver